Scientists have linked ancient great circles that predate Stonehenge to astronomy.
Scientists have for the first time proven that the 5,000-year-old great circles -- the earliest standing stone monuments in Britain that predate the Stonehenge -- were constructed specifically in line with the movements of the Sun and Moon.
Researchers at the University of Adelaide in Australia used 2D and 3D technology to construct quantitative tests of the patterns of alignment of the standing stones.
"Nobody before this has ever statistically determined that a single stone circle was constructed with astronomical phenomena in mind - it was all supposition," said project leader Gail Higginbottom, Visiting Research Fellow at the University of Adelaide.
The researchers examining the oldest great stone circles built in Scotland - Callanish on the Isle of Lewis, and Stenness on Isle of Orkney - both predating Stonehenge's standing stones by about 500 years.
They found a great concentration of alignments towards the Sun and Moon at different times of their cycles.
Two thousand years later in Scotland, much simpler monuments were still being built that had at least one of the same astronomical alignments found at the great circles.
The stones, however, are not just connected with the Sun and the Moon. Researchers discovered a complex relationship between the alignment of the stones, the surrounding landscape and horizon, and the movements of the Sun and the Moon across that landscape.
"This research is finally proof that the ancient Britons connected the Earth to the sky with their earliest standing stones, and that this practice continued in the same way for 2000 years," said Higginbottom, who is also a Visiting Research Fellow at the Australian National University.
Examining sites in detail, it was found that about half the sites were surrounded by one landscape pattern and the other half by the complete reverse.
"These chosen surroundings would have influenced the way the Sun and Moon were seen, particularly in the timing of their rising and setting at special times, like when the Moon appears at its most northerly position on the horizon, which only happens every 18.6 years," said Higginbottom.
"For example, at 50 percent of the sites, the northern horizon is relatively higher and closer than the southern and the summer solstice Sun rises out of the highest peak in the north," he said.
"At the other 50 per cent of sites, the southern horizon is higher and closer than the northern, with the winter solstice Sun rising out of these highest horizons," he added.
"These people chose to erect these great stones very precisely within the landscape and in relation to the astronomy they knew," said Higginbottom.
"They invested a tremendous amount of effort and work to do so. It tells us about their strong connection with their environment, and how important it must have been to them, for their culture and for their culture's survival," he said.
The research was published in the Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports.
![submenu-img]() Big trouble for Byju's as it looks at severe financial crisis due to...
Big trouble for Byju's as it looks at severe financial crisis due to...![submenu-img]() UP: 5 dead, several injured after 3-storey building collapses in Lucknow
UP: 5 dead, several injured after 3-storey building collapses in Lucknow![submenu-img]() Asian Hockey Champions Trophy 2024: Full schedule, fixtures, live streaming and more details
Asian Hockey Champions Trophy 2024: Full schedule, fixtures, live streaming and more details![submenu-img]() Meet self made woman of India who survived cancer, owns 10 private jets, her business is
Meet self made woman of India who survived cancer, owns 10 private jets, her business is![submenu-img]() Meet IITian who failed 7 times in work, went on to built a Rs 8398 crore company, his business is…
Meet IITian who failed 7 times in work, went on to built a Rs 8398 crore company, his business is…![submenu-img]() विनेश के सियासत में बढ़ते कदमों पर रोक, रेलवे ने नहीं स्वीकारा इस्तीफा, अब कैसे करेंगी नामंकन
विनेश के सियासत में बढ़ते कदमों पर रोक, रेलवे ने नहीं स्वीकारा इस्तीफा, अब कैसे करेंगी नामंकन![submenu-img]() Jammu-Kashmir Election: उमर अब्दुल्ला के बयान पर राजनाथ सिंह का पलटवार, 'अफजल गुरु को माला पहनाएं?'
Jammu-Kashmir Election: उमर अब्दुल्ला के बयान पर राजनाथ सिंह का पलटवार, 'अफजल गुरु को माला पहनाएं?'![submenu-img]() Bihar Politics: बिहार की राजनीति में फिर होने वाला है खेला? नीतीश कुमार की सफाई में छिपे हैं संकेत
Bihar Politics: बिहार की राजनीति में फिर होने वाला है खेला? नीतीश कुमार की सफाई में छिपे हैं संकेत![submenu-img]() दिल्ली शराब घोटाले में CBI ने आखिरी चार्जशीट रखी सामने, केजरीवाल के शामिल होने को लेकर दी बड़ी जानकारी
दिल्ली शराब घोटाले में CBI ने आखिरी चार्जशीट रखी सामने, केजरीवाल के शामिल होने को लेकर दी बड़ी जानकारी![submenu-img]() 'ग्राहक यादव, दलित, किसी भी जाति का हो सकता था, वो डकैत था'... मंगेश यादव के एनकांउटर पर CM योगी का अखिलेश को जवाब
'ग्राहक यादव, दलित, किसी भी जाति का हो सकता था, वो डकैत था'... मंगेश यादव के एनकांउटर पर CM योगी का अखिलेश को जवाब![submenu-img]() Skoda-Auto Volkswagen India to invest Rs 15000 crore to set up EV plant in…
Skoda-Auto Volkswagen India to invest Rs 15000 crore to set up EV plant in…![submenu-img]() Hyundai Venue E+ with electric sunroof launched in India; price starts at Rs…
Hyundai Venue E+ with electric sunroof launched in India; price starts at Rs…![submenu-img]() DNA Auto Awards 2024: Maruti Suzuki Swift nominated for ‘CAR OF THE YEAR’; check price, features
DNA Auto Awards 2024: Maruti Suzuki Swift nominated for ‘CAR OF THE YEAR’; check price, features![submenu-img]() DNA Auto Awards 2024: Hyundai Alcazar Facelift nominated for ‘CAR OF THE YEAR’; check details
DNA Auto Awards 2024: Hyundai Alcazar Facelift nominated for ‘CAR OF THE YEAR’; check details![submenu-img]() Hyundai Creta Knight Edition launched in India: Check price, features, design
Hyundai Creta Knight Edition launched in India: Check price, features, design![submenu-img]() Meet IIT topper who left corporate job to become IAS officer, failed four times in UPSC exam, he is...
Meet IIT topper who left corporate job to become IAS officer, failed four times in UPSC exam, he is...![submenu-img]() BIG UPDATE! UGC NET answer key 2024 to be released soon at...
BIG UPDATE! UGC NET answer key 2024 to be released soon at...![submenu-img]() Meet woman, mill worker’s daughter who lost mother during UPSC preparations, still cracked it with AIR 14, she is now...
Meet woman, mill worker’s daughter who lost mother during UPSC preparations, still cracked it with AIR 14, she is now...![submenu-img]() Meet man, 54-year-old engineer who left his high-paying job to crack NEET exam but there's a twist
Meet man, 54-year-old engineer who left his high-paying job to crack NEET exam but there's a twist![submenu-img]() Meet IIT-JEE topper with AIR 1, who quit IIT Bombay after a year due to...
Meet IIT-JEE topper with AIR 1, who quit IIT Bombay after a year due to...![submenu-img]() Mumbai: Fire Breaks Out At Times Tower In Mumbai, 9 Fire Units Deployed
Mumbai: Fire Breaks Out At Times Tower In Mumbai, 9 Fire Units Deployed![submenu-img]() 'Dharavi Project Is About Restoring Dignity...', Says Gautam Adani | Dharavi Redevelopment Project
'Dharavi Project Is About Restoring Dignity...', Says Gautam Adani | Dharavi Redevelopment Project![submenu-img]() Kolkata Doctor Case: CBI Visits RG Kar, Seizes Documents On Funds Used During Sandip Ghosh’s Tenure
Kolkata Doctor Case: CBI Visits RG Kar, Seizes Documents On Funds Used During Sandip Ghosh’s Tenure![submenu-img]() Giriraj Singh Attacked: Union Minister Giriraj Singh Assaulted In Begusarai, Bihar; Accused Arrested
Giriraj Singh Attacked: Union Minister Giriraj Singh Assaulted In Begusarai, Bihar; Accused Arrested![submenu-img]() Haryana Assembly Election 2024: Haryana Assembly Election Date Changed, Check Details Here
Haryana Assembly Election 2024: Haryana Assembly Election Date Changed, Check Details Here![submenu-img]() Big trouble for Byju's as it looks at severe financial crisis due to...
Big trouble for Byju's as it looks at severe financial crisis due to...![submenu-img]() Meet self made woman of India who survived cancer, owns 10 private jets, her business is
Meet self made woman of India who survived cancer, owns 10 private jets, her business is![submenu-img]() Meet IITian who failed 7 times in work, went on to built a Rs 8398 crore company, his business is…
Meet IITian who failed 7 times in work, went on to built a Rs 8398 crore company, his business is…![submenu-img]() This college turned down Gautam Adani’s application, after 46 years called to honour him
This college turned down Gautam Adani’s application, after 46 years called to honour him![submenu-img]() Business heartthrob Vaibhav Maloo pursues his childhood dreams in the digital world by launching InfoProfile
Business heartthrob Vaibhav Maloo pursues his childhood dreams in the digital world by launching InfoProfile ![submenu-img]() Meet Yesha Sagar, Indian-Canadian model and actress making waves as cricket presenter
Meet Yesha Sagar, Indian-Canadian model and actress making waves as cricket presenter![submenu-img]() Meet actress who never got lead roles, still turned superstar, one rumour ruined her career, became second wife of...
Meet actress who never got lead roles, still turned superstar, one rumour ruined her career, became second wife of...![submenu-img]() Sundar Pichai to Mark Zuckerberg: 10 tech leaders from Time's 2024 AI 100 list
Sundar Pichai to Mark Zuckerberg: 10 tech leaders from Time's 2024 AI 100 list![submenu-img]() Meet actress worth Rs 10000 cr, among youngest billionaires ever, once had no money for gas, now richer than SRK, Salman
Meet actress worth Rs 10000 cr, among youngest billionaires ever, once had no money for gas, now richer than SRK, Salman![submenu-img]() Top six signs of high cholesterol on face that you must not ignore
Top six signs of high cholesterol on face that you must not ignore ![submenu-img]() UP: 5 dead, several injured after 3-storey building collapses in Lucknow
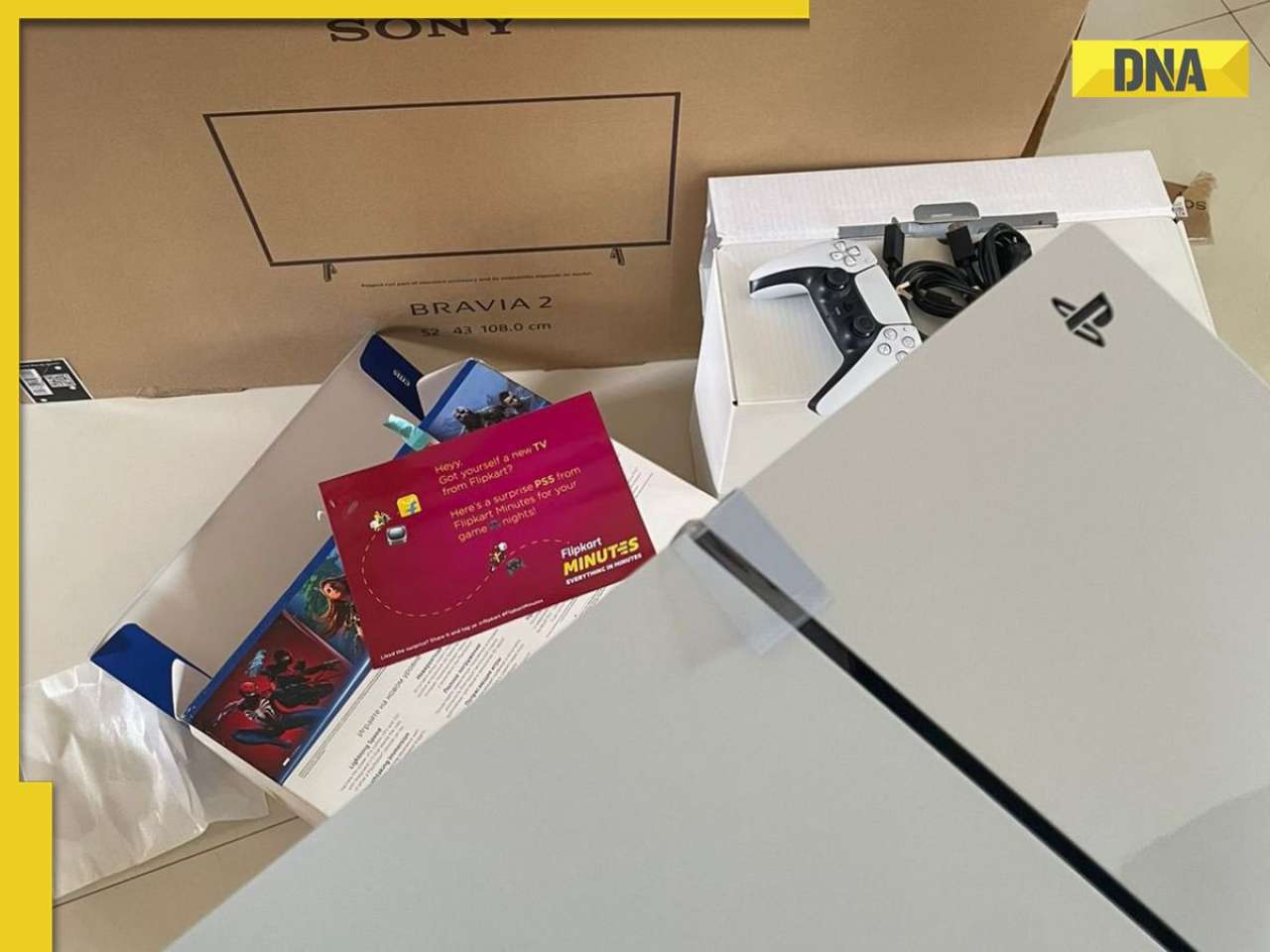
UP: 5 dead, several injured after 3-storey building collapses in Lucknow![submenu-img]() Is Flipkart Minutes the new Santa? Bengaluru man gets free PS5 with TV order
Is Flipkart Minutes the new Santa? Bengaluru man gets free PS5 with TV order![submenu-img]() CM Himanta Biswa Sarma sets this condition for new Aadhaar card applicants in Assam
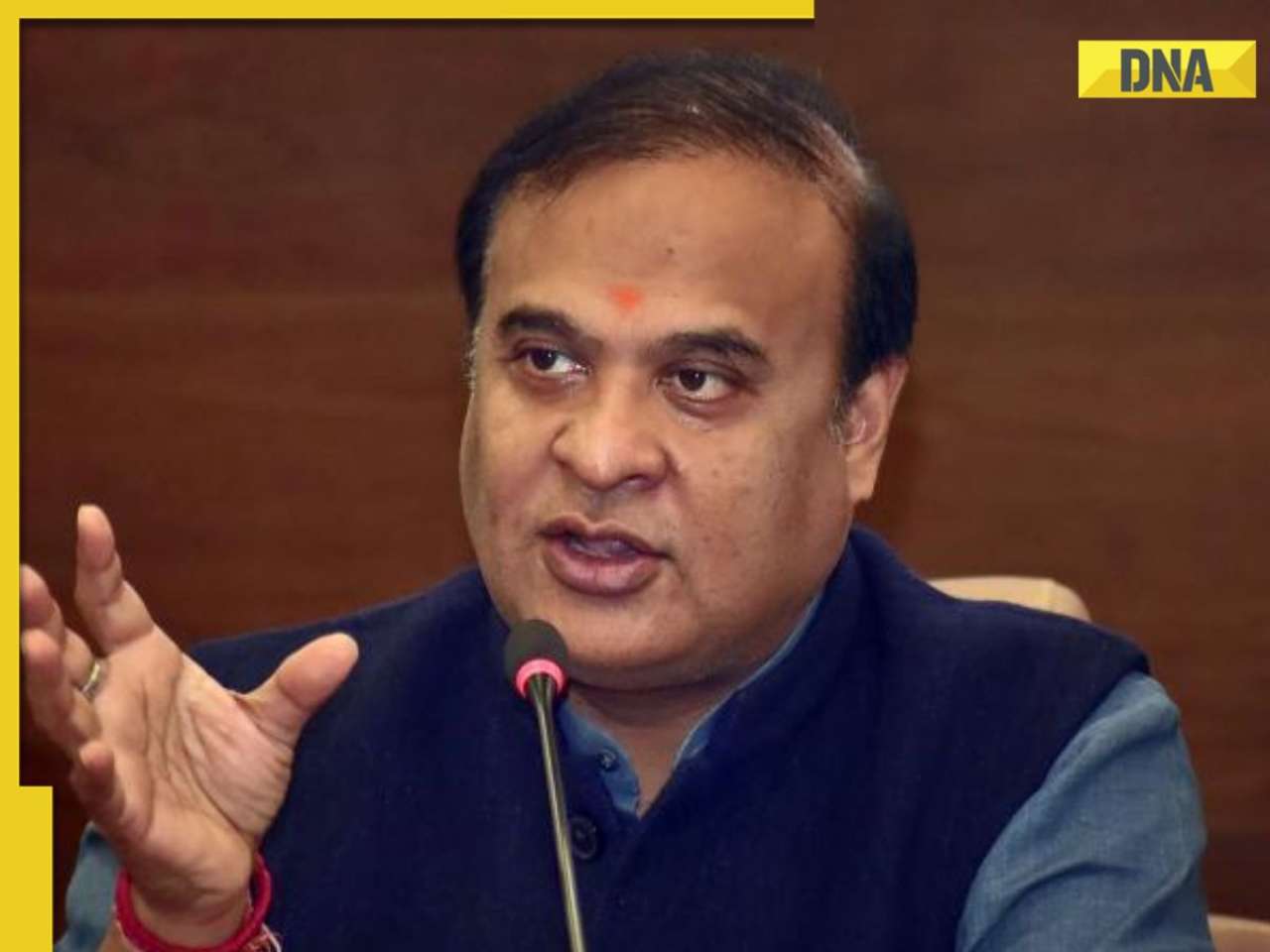
CM Himanta Biswa Sarma sets this condition for new Aadhaar card applicants in Assam![submenu-img]() Government discharges Ex-IAS Trainee Puja Khedkar over examination fraud with immediate effect
Government discharges Ex-IAS Trainee Puja Khedkar over examination fraud with immediate effect ![submenu-img]() Kolkata doctor rape-murder case: DNA report suggests Sanjay Roy lone accused, CBI to file chargesheet
Kolkata doctor rape-murder case: DNA report suggests Sanjay Roy lone accused, CBI to file chargesheet









































)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)





)
)
)
)
)
)